Ansoff's Matrix - 3.1.2
Ansoff Matrix - The Ansoff is a famous strategic maketing planning tool that helps a business determine its product and market growth strategy.
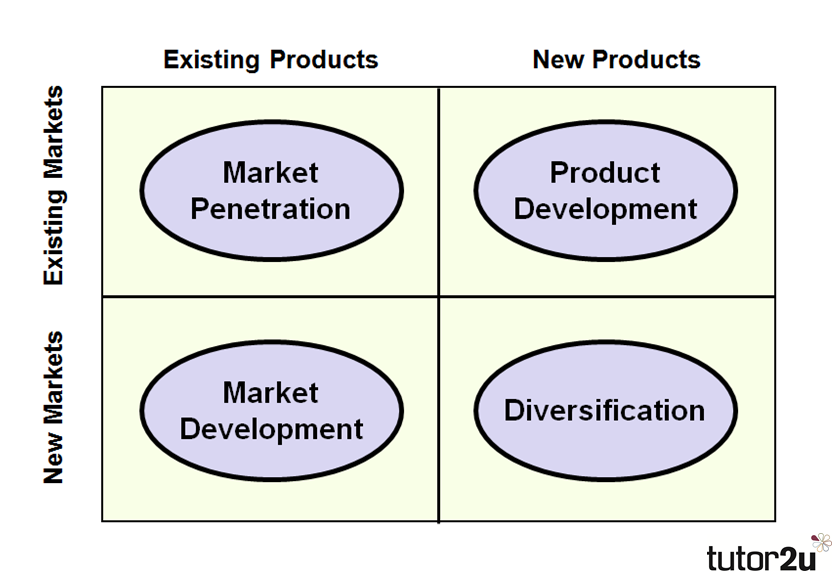
The matrix identifies four alternative growth strategies to product and market strategy based around whether a business chooses to focus on existing/new products and existing/new markets and the relationship between risk and reward.
This is a growth strategy where a business aims to sell EXISTING products to EXISTING markets.
Key Points:

The matrix identifies four alternative growth strategies to product and market strategy based around whether a business chooses to focus on existing/new products and existing/new markets and the relationship between risk and reward.
MARKET PENETRATION
This is a growth strategy where a business aims to sell EXISTING products to EXISTING markets.
Key Points:
- Trying to sell more of an existing product/service to the same target audience
- LIMITED RISK = limited potential reward also.
- Getting existing customers to buy more
- Widen the range of existing products
- Gain market share from competitors through competitive pricing or advertising
- Changes to the marketing mix e.g. loyalty scheme to increase repeat customers
- Extension strategies
- Business focuses on markets and products it knows well
- Can exploit insights on what customers want (and competition)
- Unlikely to need significant new market research
- Relatively short term only
- Market may already be saturated
- Competitors may not like this new strategy
MARKET DEVELOPMENT
This is a growth strategy involves a business seeking to sell its EXISTING products into NEW markets.
Key points:
- Attracting new customers to buy existing products
- Risk associated with lack of knowledge of customers
- New geographical markets e.g. exporting to emerging markets
- New distribution channels (e.g. using e-commerce or mail order)
- Different pricing policies to attract new customers in different segments
- A logical strategy where existing markets are saturated or in decline
- Bring in greater rewards than market penetration
- Often riskier than product development - particularly expanision into international markets
- The business may not understand the market
- Alienation of current customers
- Existing products may not suit new markets: depends on customer needs
PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
This is a growth strategy where a business aims to introduce NEW products into EXISTING markets.
Key points:
- Selling new and better products to existing customers
- Risk = not knowing the products, high R&D costs
- This strategy is driven by investment in new product development
- Usually requires consistent, long-term investment in R&D so that it can appeal to the existing market
- Technological innovation provides significant opportunities for product development strategies
- Brand extensions are also examples of product development
- This is a strategy that often plays to the strengths of an established business
- Strong emphasis on effective market research (insights into customer needs) and successful innovation
- A great way of exploiting the existing customer base who may respond positively to new products
- Can launch substantially improved versions of existing products
- Introduce complementary products
- May shorten PLC of existing products,for example as soon as Apple released the Iphone 7, sales of the Iphone 6 started to decline.
- Damage to brand if product the new and better products are not as good as the original.
DIVERSIFICATION
This is a growth strategy where a business markets NEW products in NEW markets
Key Points:
- Innovation and R&D develop new solutions
- High risk strategy as 2 elements are unknown, the market and the product
- High risk but also greatest reward potential
- Acquire an existing business in the market
- Extend an existing brand into the new market
- If successful, overall risk of the business is spread and rewards are huge
- If one market is stagnant, another may well be growing, preventing a business from an overall decline in performance.
- Inherently risky strategy
- No direct experience of the product or market
- Few economies of scale (initially)
- Relies on heavy investment
- Cultural differences may apply
- Brand name may be diluted
Comments
Post a Comment